Home \ Low Carbon School Pilot Project \ What is the Impact of Climate Change on Biodiversity?!
May 22 is the International Day for Biological Diversity, which is the international theme day proposed by the United Nations Environment Programme for sustainable utilization and protection of biodiversity.

As we all know, biodiversity is the foundation of life on earth and the precious wealth of human development. A healthy and dynamic ecological environment can provide important ecosystem services for human beings, such as our indispensable food, fresh water resources, air and energy.
Loss of biodiversity will break the balance of ecological environment and lead to climate disasters, which will aggravate food crisis, resource depletion and even threaten human health.

Picture Source:unsplash
With the deterioration of environmental problems caused by the destruction of biodiversity, "Environment Day" has been paid more and more attention to. People are afraid of the disastrous impact of climate change, focusing on how to protect biodiversity from destruction.
But in fact, do you really know how climate change and biodiversity interact?
Climate change seriously affects biodiversity at different levels
Large number of studies have shown that large-scale climate change has a serious impact on biodiversity at different levels. For example, climate change has exacerbated the loss and fragmentation of habitats, affecting more than 18% of continental ecological habitats, in which more than 50% of terrestrial vertebrates live.
In addition, the statistical data also shows that a large number of animals start to move towards the poles due to the warming of the environment. Without obstacles, the average speed of these animals on land reaches 17km every 10 years, while the average speed in the ocean is as high as 72 km every 10 years.

Picture Source:unsplash
Climate change will also affect the seasonal pattern of plants and animals. In order to adapt to climate change, they began to change seasonal flowering, migration, reproduction and other periods, and these changes also affected the food chain of the whole ecosystem. For example, predators at the relatively top of the food chain may also face food shortages due to changes at the bottom, leading to a decline in the number of predators.
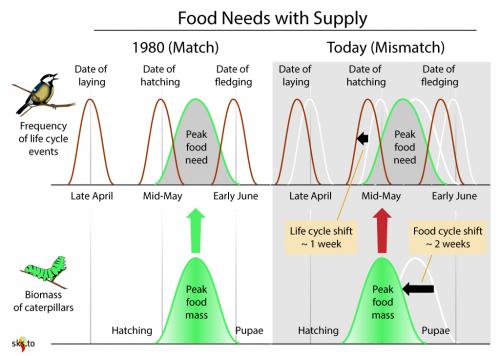
20 years ago, birds hatched to be fed by worms. Now this "natural agreement" has weakened, and the birds will starve after hatching. Picture source: SkepticalScience
In fact, the impact of climate change on biodiversity will vary with the number and extent of populations, geographical location, species groups, time and adaptability. But on a global scale, climate change in the 21st century is putting a large number of species living in oceans, rivers and on land at risk of extinction.
According to the United Nations Environment Programme, more than 70% of coral reefs will die if the global average temperature rises by 1.5 ° C; and more than 99% of coral reefs will die by 2050 if global warming rises by 2 ° C.
In the nearly 550 million years of its existence, the earth has experienced five mass extinctions. Mass extinction or cluster extinction refers to an event in which the number and species of organisms decrease sharply in more than one and larger geographical area during a relatively short geological period. Scientists speculate that 98% of the creatures that had appeared since the birth of the earth have been extinct.
Professor Chris Johnson of the University of Tasmania in Australia, said that since the asteroid impact that wiped out dinosaurs and many other species 66 million years ago, the extinction rate is the highest now, which is closely related to human activities and climate change caused by human activities.
"Regional ecosystems are in danger of collapse, we are in the sixth mass extinction."said Gerardo Ceballos, a professor of the National University of Mexico. According to our research and the evidence of our eyes, the extinction crisis is very serious, and the behavior of all of us in the next 10 to 50 years will determine the future of mankind. "

Picture Source: upsplash
At the same time, another effect of climate change is more frequent extreme weather.
In the long run, it is challenging the carrying capacity of ecosystem and increasing the vulnerability to natural disasters. Very dry and hot areas are likely to suffer from sustained heat waves and droughts, making water shortage more serious. A series of changes caused by these abiotic factors not only change the suitability of the original habitat of species, but also provide opportunities for some invasive species.
Biodiversity also affects climate change
Similarly, biodiversity can effectively increase the resilience of ecosystems.
By restoring the important functions and services provided by ecosystems, the impact of climate change can be greatly reduced. Meanwhile, more carbon can be fixed, which will slow down climate change.
In addition, some key species play an important role in maintaining the structure of ecological community. For example, in forest protection, anteaters can prevent termites from eating trees and damaging forests. The African forest elephant, which is listed as an extremely endangered species by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), plays a significant part in the growth of large trees and the maintenance of a healthy forest ecosystem, helping forests absorb more carbon.

Picture source: WWF
Because the impact of climate change on human beings is largely transmitted through the natural system, climate change can shake the economy and society through its impact on the ecosystem. Healthy ecosystems are more resilient to climate change and therefore more capable of sustaining our prosperity and well-being.
Protect biodiversity and tackle climate change at the same time
Climate change and biodiversity loss are twins. So can we tackle them together?
The answer is yes!
Reducing anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions rapidly can mitigate climate change effectively, which is a fundamental contribution to the protection of ecosystems and biodiversity. Meanwhile, protection of biodiversity is also essential for mitigating and adapting to climate change.
According to IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) and Oxford University, the NbS(Nature-based solutions) are conducive to climate and biodiversity, contributing about 40% of CO2 emission reduction by 2030, and providing a good opportunity to control global warming below 2 ℃. For example, forests and peatlands are indispensable habitats as well as important carbon storage sites.Protecting forests and peatlands not only maintains the biodiversity, but also reduces the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. As extreme weather events aggravated by climate change, forests and peatlands can also play a positive role in regulating and slowing down.

Rethinking the relationship between nature and climate change: biodiversity will become vulnerable due to climate change, but protecting biodiversity will make it a powerful helper for us to deal with climate change. Picture source: IUCN(International Union for Conservation of Nature)
Although most of the solutions can kill two birds with one stone, it is inevitable that some climate change mitigation measures may conflict with the goal of biodiversity conservation, and vice versa. Therefore, the assessment of mitigation and adaptation to climate change and biodiversity conservation measures need to be comprehensive and systematic.
Authors: He Mu, Liu Jian, volunteers of low carbon project
Auditor: Ding Zejun, Gao Lianrui
Reference:
https://www.who.int/globalchange/ecosystems/biodiversity/zh/
https://www.un.org/zh/observances/biological-diversity-day
https://www.pnas.org/content/117/49/30882#sec-2
https://portals.iucn.org/library/node/48525
https://www.unep-wcmc.org/news/tackling-climate-change-and-biodiversity-loss-together
Project introduction:
Yunnan Low-carbon Schools Pilot Project is funded by the European Union and implemented by the People to People Foundation (Spanish member of HPP) in cooperation with FAIHPP (Switzerland) Yunnan Representative Office, Yunnan Academy for Science and Technical Information, Southwest Forestry University, Chinese Youth Climate Action Network, Green Kunming (Kunming Environmental Popular Science Association) and Kunming Good Deed Public Welfare Community Development Service Center with a project cycle from January 1, 2020 to December 31, 2023. The project begins by increasing partners’ awareness and advocacy on climate change mitigation and environmental protection, by raising climate change awareness among 600 schools, 70,000 students and teachers, determine the emission benchmark through basic calculation, and then implement emission reduction work in 50 Carbon Compliant Pioneer Schools. Use science, technology, innovation and other means to respond to “climate action” to accelerate environmental sustainability and promote the transition from green campuses to low-carbon and carbon-neutral campuses.

The project is funded by European Union.

Any views or opinions presented are solely those of the author, and do not necessarily represent those of the donor.